WEEK ONE
Currents trends of VFX:
Real-time technology, LED volumes, virtual production, facial recognition, volumetric capture, technical collaborations are examples of the most common current trends in the VFX. This makes the VFX industry rapidly expand so globalisation, outsourcing, collaboration and remote workflows are used widely and steadily in VFX. AI seems to be taking over every aspect of VFX creating new efficiencies and creative possibilities.
- Anime using CGI – failure frame
- Real rendering
- De-aging (captain marvel)
- Surrealism (horror) (dreams)
- Deep fakes – seen in film Book of Boba fet
Today we are in the ‘Age of Image’. James Fox states:
“We are a population of image addicts, we now take more photographs every minute than were made in the entire 19th century” (Fox, 2020)
Taking pictures is easily accessible so people take pictures during their everyday routine of their everyday life. As social media gives everyone a platform, everyone wants to share their life. Instead of only relying on Google Images to find pictures, a platform that can be considered generic and has a lack of meaning, pictures taken by oneself or perhaps of oneself has a personal story behind it and therefore added value/worth.


.jpg?mode=max)
HAROLD EDGERTON WORK SEEN IN TODAYS FILMS
The matrix

Sherlock Holmes – 2010


Dredd – 2012

HOMEWORK
“What does Dr. Fox mean by ‘The Age of the Image’?”
In “The Age of the Image,” Jamie Fox means that we live in a time when visuals—like photos and videos—greatly influence how we see the world and understand events. He emphasizes that these images can shape perceptions, identities, and even societal attitudes, urging us to think critically about what we see.
A powerful scene addresses the aftermath of 9/11, showcasing the profound impact of imagery on public perception. Fox highlights how iconic images from that tragic day—such as the collapsing towers and the responses of first responders—shaped American consciousness and national identity. This scene serves as a critical lens through which to understand the documentary’s central theme: the significant role visual media plays in constructing collective narratives.
The relentless replay of 9/11 imagery evokes strong emotional responses, influencing societal attitudes toward safety, fear, and community. Fox illustrates how these visuals not only documented a historical moment but also molded public sentiment, reinforcing the idea that in “the age of the image,” our understanding of significant events is increasingly mediated by the visuals we consume.
Moreover, Fox addresses the darker side of this imagery, particularly concerning its impact on marginalized communities. The portrayal of Muslims post-9/11 exemplifies how powerful images can perpetuate harmful stereotypes, leading to misconceptions and societal division. This duality reflects the documentary’s exploration of representation and the responsibility that comes with visual storytelling.
Ultimately, Fox’s examination of the 9/11 scene encapsulates his message about “the age of the image”: it reveals how images shape our understanding of reality and influence personal and collective identities. By criticallly engaging with these visuals, Fox urges viewers to recognize the power of imagery in shaping narratives and the importance of responsible representation in a visually driven world. It is crucial to recognize that this power can fall into the hands of the wrong individuals, granting them the ability to manipulate societal perceptions. Therefore, it’s essential to question and critically evaluate what we see rather than accepting it at face value.
WEEK TWO
The Photographic Truth – Claim
The Allegory of the Cave – A philosophical concept created by Plato that explores the nature of reality, perception and knowledge. It follows the story of a group of prisoners stuck in a cave who are made to believe that shadows are real people until one of them escapes and comes to realise that the shadows were actually real people. This represents the journey from ignorance to enlightenment.
How does Plato’s Allegory of the Cave reflect through visual effects?
- Video games/ virtual reality
- Compositing
- Photoshops
- Simulations
- Filters
Seamlessness is a key aspect in the illusion of reality. In order to make the aspect more real vfx are designed to blend seamlessly.
Hyperrealism is where VFX can create hyper-real versions of reality that seem plausible but are in actual fact hindered using software. This can trick viewers into believing in alternate realities or even questioning their own perceptions.

September 11th 2001 – Twin Tower Attack
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/destruction-white-house-down-dd7e42e9b5604a98aa6b2e734a7f1147.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/destruction-armageddon-cb0c58a1e0c84b729d05a5c45862c93b.jpg)
Armageddon
What is meant by The Photographic Truth Claim?
Photographic truth refers to the extent photographs capture reality in the absence of image manipulation. Despite the claim, whether it captures authenticity is debated as concepts of representing aesthetics are challenged (Fiveable, n.d.). Issues arise surrounding indexicality and the nature of the truth claim. Indexicality is challenged through how cameras capture, store and transfer images, leading to manipulation. This challenges the notion of photographic truth as despite the appearance of reality, several factors such as light intensity and the storage of information, dependent on the camera, alter the image in comparison. Processes such as exposure rate, shutter types, developing and printing the image and lens type all play a role in manipulating the image, removing the authenticity and classification of it being reality (Gunning, 2004, p. 40). Furthermore, it is noted that ‘photographic truth are reliant on interpretation and contextualisation’ in which it cannot exist independently without acknowledging the context of experience, interpretation and ideas (Porter & Kennedy, 2012, p. 187). This further clarifies the meaning of photographic truth and the critical engagement surrounding the discourse of conveying reality and experience. Considering the increasingly manipulative stages throughout the photographic process, and the reliance upon context, the nature of the truth claim is undeniably up for interpretation. Viewing images to reflect reality subjectively or objectively is in the eye of the beholder, whether you recognise the role the digital or film-based camera plays in exposure rates and light intensity, or subjectively perceive the image as ‘real’ within the context it is conveyed to you.
WEEK 3 – Faking photographs – Image Manipulation & Computer Collage
Faked Analogue Photographs
Historical examples of analogue photos from before the digital age:
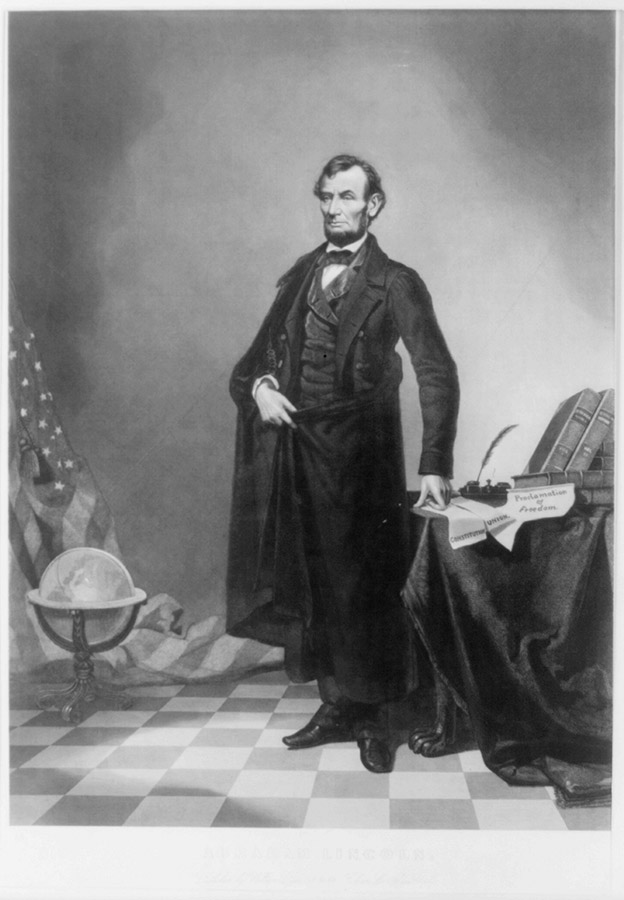

The head of Abraham Lincoln is superimposed on the figure and background of an earlier print by A.H. Ritchie showing John C. Calhoun, 1852.
Famous faked digital photographs (now proven to be fake) that were manipulated using digital tools like Photoshop:

AI-generated images of former US president Donald Trump getting arrested went viral in March 2023 after Twitter user Eliot Higgins decided to generate them for visualisation purposes after reading about Trump’s indictment.
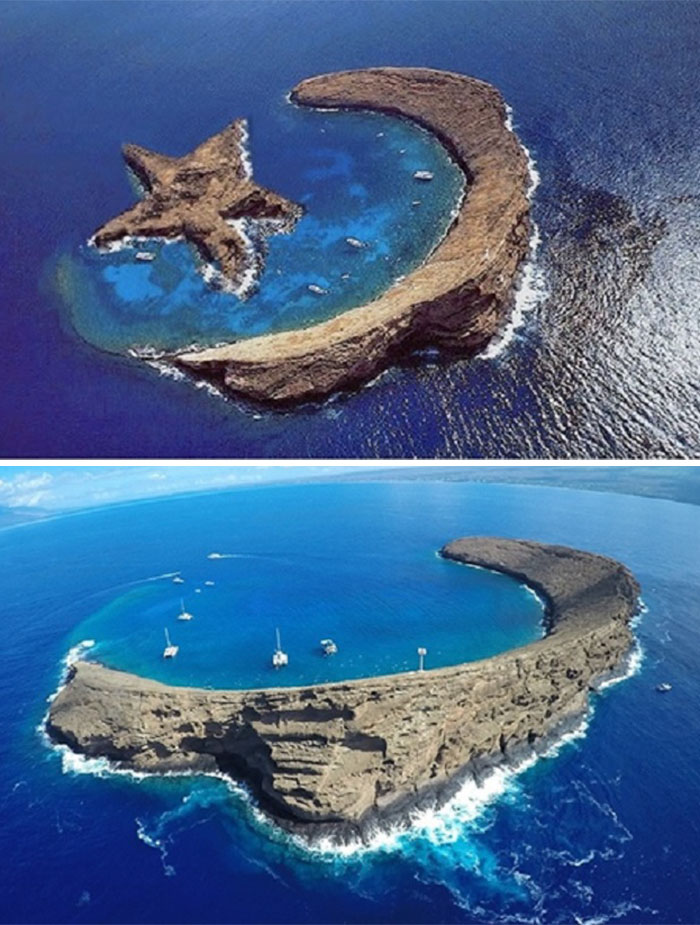

An Island That Looks Like A Star – Photoshopped#


MONEY HEIST – VFX breakdown





DEFINE COMPOSITING THEN EXPLORE THE EXAMPLES
Compositing is used in film and video production to compile visual elements from different sources to create a single image. VFX editors’ job is to make this look seamless and give the illusion that all elements are initially part of the same scene. I will provide two films where this is shown in an unnoticeable manner and break it down.
First example – Black Swan
Removing film crew
Identify the Components:
VFX crew used advanced compositing techniques to carefully remove any unintended reflections or to create a certain ambience or effect as seen in the first example by blurring the floor to make it appear more angelic.
Optics & Perspectives:
In the scene where the film crew is being hidden, I think was done very seamlessly. They managed to recreate elements of the reflected space digitally and composited them onto the mirrors surface, creating a perfect imitation of the actual set.
Believability in Composition:
These are all examples of compositing that are subtle and would not have been noticed if not pointed out. This is achieved by using the correct shadowing, lighting and colouring. In the first example they mixed composited parts with the live-action footage, motion blur and film grain made compositing appear undetectable. Certain kinds of grain and blur that naturally appear in films are familiar to our senses. To make the composited portions seem seamless, the VFX crew meticulously matched these components to the source video.
Rule of Thirds:
The rule of thirds played a crucial role in compositing the mirror scene by placing Nina’s reflection precisely along the vertical third line, which aids in guiding the audience’s attention naturally between her physical and reflected self without the viewer consciously noticing the VFX work.
Week 4 – The Trend of Photorealism
FOUR EXAMPLES OF PHOTOREALISM IN CGI
Love, Death and Robots – Lucky 13


Love, Death and Robots – Sonnie’s Edge

King Kong Skull Island

Rendered images


Gemini Man

What is Photorealism? – 250 words
Photorealism is a ‘mode of representation’ of depictions within media, created through a ‘computer-graphics image’ to look as if it was photographed, applying realistic processes to enhance the realism of an event. This can often be applied depictions of events that cannot be measured based upon its reality due to absence of existing representations. Without a benchmarking capability, how can a depiction of something be constructed to appear real? Using special effects, photography ‘creates a reality effect’, notably used in Terminator 2 and The Matrix (Joon, 2010, p.18; Lister, M. et al., 2009, p. 137). Several principles of photorealism act as a guideline to achieve rendering objectives. This includes, clutter and chaos, personality and expectations and surface texture. The importance of these guidelines and principles stems from the objective to attain enhanced performance of a 3D model that will strengthen application and expect improved outcomes. Certain factors come into play in adjusting the right qualities to produce the expected results of reality. In this instance, lighting is incredibly significant, such as global illumination and dome lighting. Global illumination has the potential to describe events through lighting as it would in actual reality, considering indirect and direct illumination. On the other hand, dome lighting portrays a skylight effect, stimulating soft shadows, appearing as ‘an overcast day’ (Joon, 2010, p. 19). These principles are crucial to follow to enhance the realism of photography and filmmaking, and in doing so will portray events that capture experiences and emotions for an audience incapable of acquiring such depth due to lack of existence and inability to experience it.
WEEK 5 – Digital Index : Bringing indexicality to the capture of movement
Comparing motion capture and keyframe animation:
While both motion capture (mo-cap) and keyframe animation are methods for producing stylized or realistic movement, they differ in approach and application. Motion capture records the movement of people or objects, specifically the actions of actors, to create animated digital characters in 2D or 3D. Keyframe animation, on the other hand, involves manually setting specific positions (keyframes) for an object or character at certain points in time, giving the animator control over the movement for smooth, stylized results. Motion capture is effective for capturing natural human movement quickly and efficiently, while keyframe animation is better suited for artistic and stylized work, offering complete creative control. In modern VFX, both techniques are often combined to balance realism with artistic freedom. However, motion capture is preferable for specific tasks. For example, a keyframe animator would struggle to replicate an actor’s signature move, but motion capture excels at this. In *The Lord of the Rings: The Two Towers* (2002), Gollum’s character was created using motion capture, enabling animators to replicate his nuanced movements and expressions realistically. Keyframing can take a week to complete, and if the director requests changes, the animator must redo the work. In contrast, motion capture allows for real-time adjustments, making it easier to modify the movement or direct the actor on the spot .In conclusion, motion capture is often the preferred choice due to its advanced technology and ability to replicate real-life movements accurately and efficiently.
Describe/define motion capture and key framing – Advantages, disadvantages? When and what character might use traditional key-frame technique? When and for what character might motion capture be used? 250 words
WEEK 6 – Reality Capture (LIDAR) and VFX through 3D scanning
Reality Capture is an umbrella term for the technologies and practice of 3D scanning
Examples of 3D scanning
- Depth-based screening
Depth Scanner allows you to create depth maps from images and videos. The resulting depth map can be used for a variety of post processing tasks, like adding fog, converting footage to stereo-3d and many more image effects.

- Laser scanning
Laser scanning is a method of 3D modeling that uses laser beams to measure the time it takes for the laser pulses to bounce back from a target object or surface.
- Lidar Scanning – TYPE OF LASER SCAN
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing technology that uses laser beams to measure distances and movement in real time.

- Photogrammetry – TYPE OF LASER SCAN
Type of laser scan that delivers 3d object by combining multiple photos of it. Can be used for small objects to large buildings.

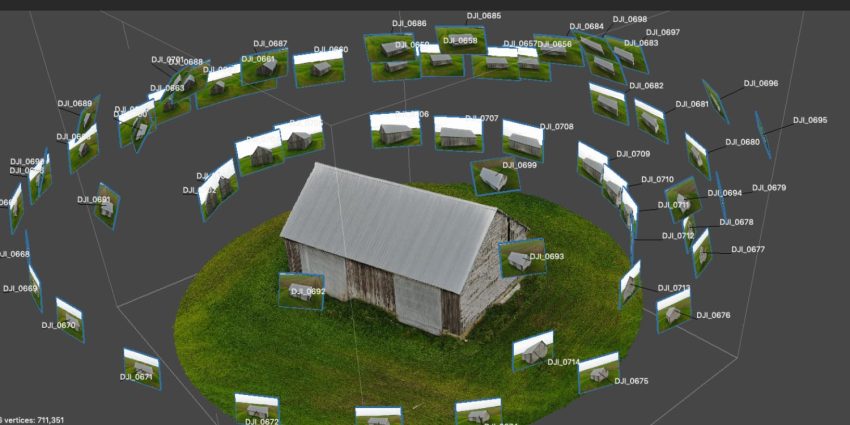
Main differences between Photogrammetry and LIDAR 3d scanning are
- Photogrammetry uses photographs taken from different angles where as LIDAR uses laser beams to scan the environment.
- LIDAR provides highly accurate and detailed 3D measurements of surfaces including factors such as contours and spatial geometry whereas Photogrammetry captures more visual detail such as textures, patterns and colours but less accurate when it comes to precise measurements.
CASE STUDY – 250 words on Reality Capture
Reality capture, the process of digitally documenting real-world environments, utilizes advanced technologies like 3D scanning, photogrammetry, and drones to generate detailed 3D models. These tools are essential for high resolution 3d models that are utilise by various industries including film, architecture, construction and archaeology. VFX artists are able to accurately replicate real-life objects and settings in digital environments. This method makes it possible for filmmakers and game designers to smoothly integrate live-action video with digital effects by including realistic, high-resolution models into their scenes. A good example of this is Avengers: Endgame (2019), where 3D scanning was used extensively to create digital doubles of actors for action sequences, . The film featured complex VFX shots using digital replicas of characters, especially in scenes with heavy CGI environments, such as space battles or fight sequences. 3D scanning allowed for detailed, lifelike representations of the actors, ensuring that their digital doubles matched their physical counterparts in movement, lighting, and texture. Lidar Lounge is a platform that offers 3d scanning technologies like hyper-realistic, high- resolution digital models of real-world environments. It employs advanced LiDAR scanners alongside drones to capture data with millimetre accuracy across large distances. By combining real-world and virtual filmmaking, this technology enables intricate scenes like those in The Mandalorian, where realistic environments are projected using high-resolution scanned data within digital sets. As this data gets better, it becomes harder to distinguish between digital and real, which raises questions about whether the audience’s perception of “authenticity” in movies could be weakened by such VFX hyperrealism.
WEEK 7 – Reality Capture ( Photogrammetry ) and VFX
Digital Michelangelo Project
This is a computer rendering made of a 3d model of Michelangelo’s David. One of the first 3d scans. The models contains about 1 billion polygons.
Photogrammetry was used to capture this and is widely used to create digital 3D models of historic buildings and objects, preserving them for the future. Unlike physical items, these digital scans won’t degrade over time, ensuring an accurate, lasting record
Mimesis – The act of representing or imitating reality in art.
WEEK 8 – Simulation & Hyperreality
WEEK 9 – Virtual Filmmaking
| OPTION 3: How do Spectacular, Invisible, and Seamless Visual Effects Influence Modern Filmmaking? Use examples or case studies to analyze one type of effect or compare two or more.
In your essay, you may choose to:
|
- Define Spectacular effects and invisible effects
- Compare them and include their similarities and differences
- Use examples – The Crown, Chernobyl – : The highly detailed digital recreation of the Chernobyl reactor and surrounding areas helps to add authenticity to scenes, yet many viewers won’t notice the CGI as it perfectly blends with the set and lighting. The dangerous atmosphere and environments are enhanced through invisible digital effects, adding a sense of foreboding without making it obvious. The Revenant – While The Revenant is known for its natural landscapes and intense cinematography, the film used digital effects in subtle ways: The bear attack scene, for example, combined practical effects with digital enhancements, creating a seamless interaction between Leonardo DiCaprio and the CGI bear. CGI was also used to subtly alter or enhance the natural environments, adding to the harsh, survivalist feel of the movie without it being immediately obvious. The Handmaid’s Tale is a dystopian show with subtle but highly effective visual effects: Visual Enhancements of Locations: CGI is used to extend or enhance existing locations, such as the grand cityscapes of Gilead or the barren rural settings, making them appear more isolated or oppressive. Digital Atmosphere: Visual effects are used to heighten the atmosphere, such as subtly adjusting the color grading or adding atmospheric elements like dust, fog, or sunlight to heighten the sense of tension and control.
-Relate this to photorealism and how the effects contribute to immersion, narrative development and visual storytelling
