Week 1 The basics.
Why Houdini?
Interface Overview
contexts
node tree
Attribu1 The basics. Why Houdini?
Interface Overview
contexts
node tree
Attributes
Week 1 : Project 01 – Cheese Hole.
Nodes Used and Its Explanation
-
Scatter : This node distributes new points across the surface in a roughly uniform pattern and optionally attempts to limit clumping and holes.
- Copy to Points :This is very useful for populating scenes with repeated elements such as trees, buildings, or snowflakes with full control over the placement of the copies.
Tip :- To simply create multiple copies of geometry without needing target points, use Duplicate.
For example, you can arrange copies in a spherical shape by copying them onto the points of polygonal sphere. Or you could scatter points across a terrain geometry and copy trees onto the points.
- Boolean :This node can perform several different functions according to the Operation parameter.The common operations are:
-
Boolean operations (union, intersect, subtract) between two “solid” models:
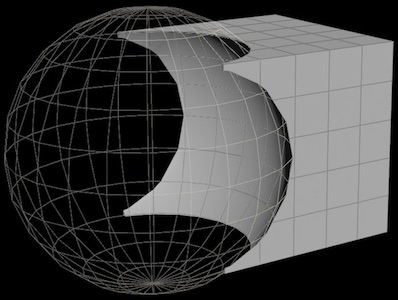
-
Shattering a solid model using cutting surfaces:
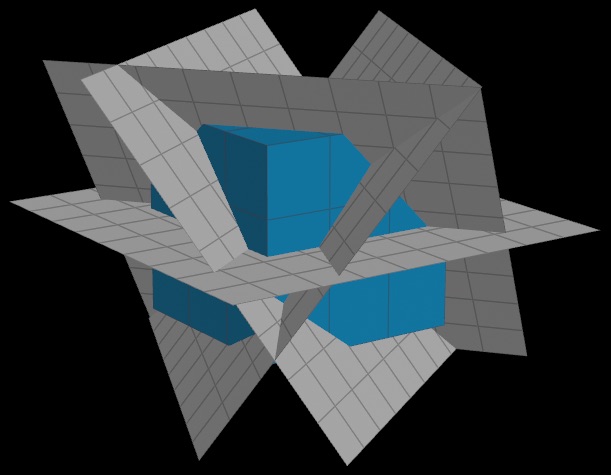
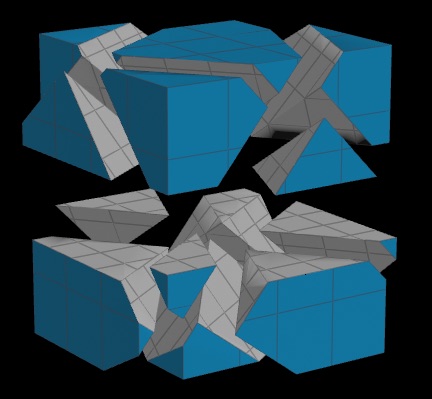
You can shatter with any number of complex cutting surfaces, allowing natural-looking, artistically controlled destruction.
-
Generating polylines along the seams where two models intersect.
-
Detecting intersections and putting intersecting polygons into groups.
You can specify the input models as “solid” (treat the model surface as if it encloses a solid filled space) or “surface” (treat the model surfaces like flat planes). Boolean (sidefx.com)
-
4. Polybavel : Creates straight, rounded, or custom fillets along edges and corners.
5. Color: Adds color attributes to geometry.
The color (Cd) attribute affects the display of the wireframe, and of faces in non-VEX shaded mode. The default shader in mantra, and many other shaders, will also use the attribute for rendering.
Week 1 : Project 02 – LEGO Piece
SOPs (Surface OPerators)
-To differentiate the types of network, Houdini uses acronyms. For FLIP fluids, there are two relevant network types: SOP stands for Surface OPerator. Inside a SOP network you find everything that’s required for constructing and modifying geometry and volumes.)
Week 2
Week 2 : Project 01 – Dominos Effect
Curve Node: Lets you interactively draw Bézier curves using tools similar to 2D illustration programs, as well as polylines and NURBS.
Box Node :
Screen Recording.
Week 4
Screen Recording .
Week 5
Week 5 : Project 02 – Moon
Week 6
Week 6 : Project 01 – Image Modelling
Week 6 : Project 02 – smoke_machine_start
Week 7
Week 7 : Project 01 – height field and drone_disaster
Week 8
Week 8 : Project 01 – Grass and Stompy_dinosaur_mud.
Week 9 : Project 01 – Grass
Week 10 : Project 01 – flamethrower
SIMON RENDER :
My Flamethrower Render.
Week 11 : Project 01 – Blood drops
Week 11 : Project 02 – Dolphin
Refrence:
Godzilla File and Texture :
Final:
Showreel




































